Introduction
As software development becomes increasingly complex, the need for effective testing strategies has never been more crucial. One powerful tool in the tester's arsenal is the sequence diagram, a visual representation of the interactions between various system components. In this blog post, we'll delve into the use of sequence diagrams for test case design, exploring how they can enhance the testing process and provide valuable insights into system behavior.
Sequence diagrams are a type of UML (Unified Modeling Language) diagram that illustrate the flow of messages between objects in a system over time. They are particularly useful for understanding the dynamic behavior of a system, making them a valuable tool for designing and documenting test cases.
The Importance of Sequence Diagrams in Test Case Design
Designing comprehensive and effective test cases is a critical aspect of software development. Sequence diagrams play a crucial role in this process by:
-
Enhancing System Understanding: By visually depicting the interactions between system components, sequence diagrams help testers gain a deeper understanding of the system's behavior, which is essential for crafting meaningful test cases.
-
Identifying Edge Cases: Sequence diagrams can reveal potential edge cases and error scenarios that might not be immediately apparent, allowing testers to proactively plan for and address these situations.
-
Improving Communication: Sequence diagrams serve as a common language for developers, testers, and other stakeholders, facilitating efficient communication and collaboration during the testing phase.
-
Traceability and Maintenance: Well-documented sequence diagrams can aid in the traceability of test cases, making it easier to maintain and update them as the system evolves.
Leveraging Sequence Diagrams for Test Case Design
To effectively leverage sequence diagrams for test case design, follow these steps:
-
Identify the Relevant Scenarios: Start by analyzing the system requirements and use cases to determine the key scenarios that need to be tested. This will help you focus your efforts and ensure that your test cases align with the system's expected behavior.
-
Document the Sequence Diagrams: Create sequence diagrams that accurately represent the interactions between the various system components for the identified scenarios. This will provide a visual reference for the expected behavior of the system.
-
Design Test Cases: Carefully examine the sequence diagrams and use the information they provide to design comprehensive test cases. Consider the following elements when creating your test cases:
- Actor/Object Interactions: Verify that the interactions between the system components are as expected.
- Message Sequence: Ensure that the order and timing of the messages exchanged are correct.
- Error Handling: Identify potential error scenarios and design test cases to validate the system's error handling mechanisms.
- Edge Cases: Analyze the sequence diagrams for edge cases and create test cases to cover these scenarios.
-
Implement and Execute Test Cases: Implement the test cases and execute them against the system. Continuously update the sequence diagrams and test cases as the system evolves to maintain their relevance and accuracy.
Practical Examples: Sequence Diagrams for Test Case Design
To illustrate the use of sequence diagrams in test case design, let's consider a few practical examples.
Example 1: User Login Scenario
Suppose we have a web application that allows users to log in. Here's a sequence diagram that depicts the login process:
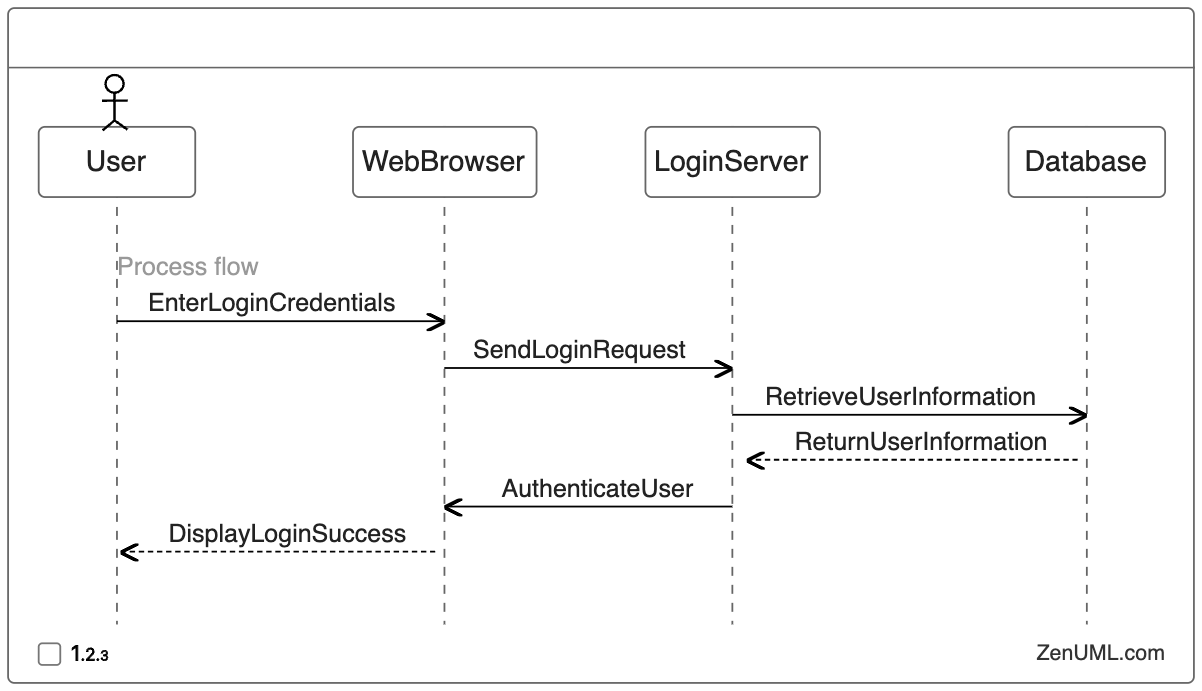
Based on this sequence diagram, we can design the following test cases:
- Valid Login: Verify that a user can successfully log in with correct credentials.
- Invalid Login: Ensure that the system rejects login attempts with incorrect credentials.
- Timeout Handling: Validate that the system handles login timeouts gracefully and prompts the user to try again.
- Database Unavailability: Test the system's behavior when the database is unavailable during the login process.
Example 2: Online Shopping Checkout Process
Consider an online shopping application with a checkout process. Here's a sequence diagram for the checkout flow:
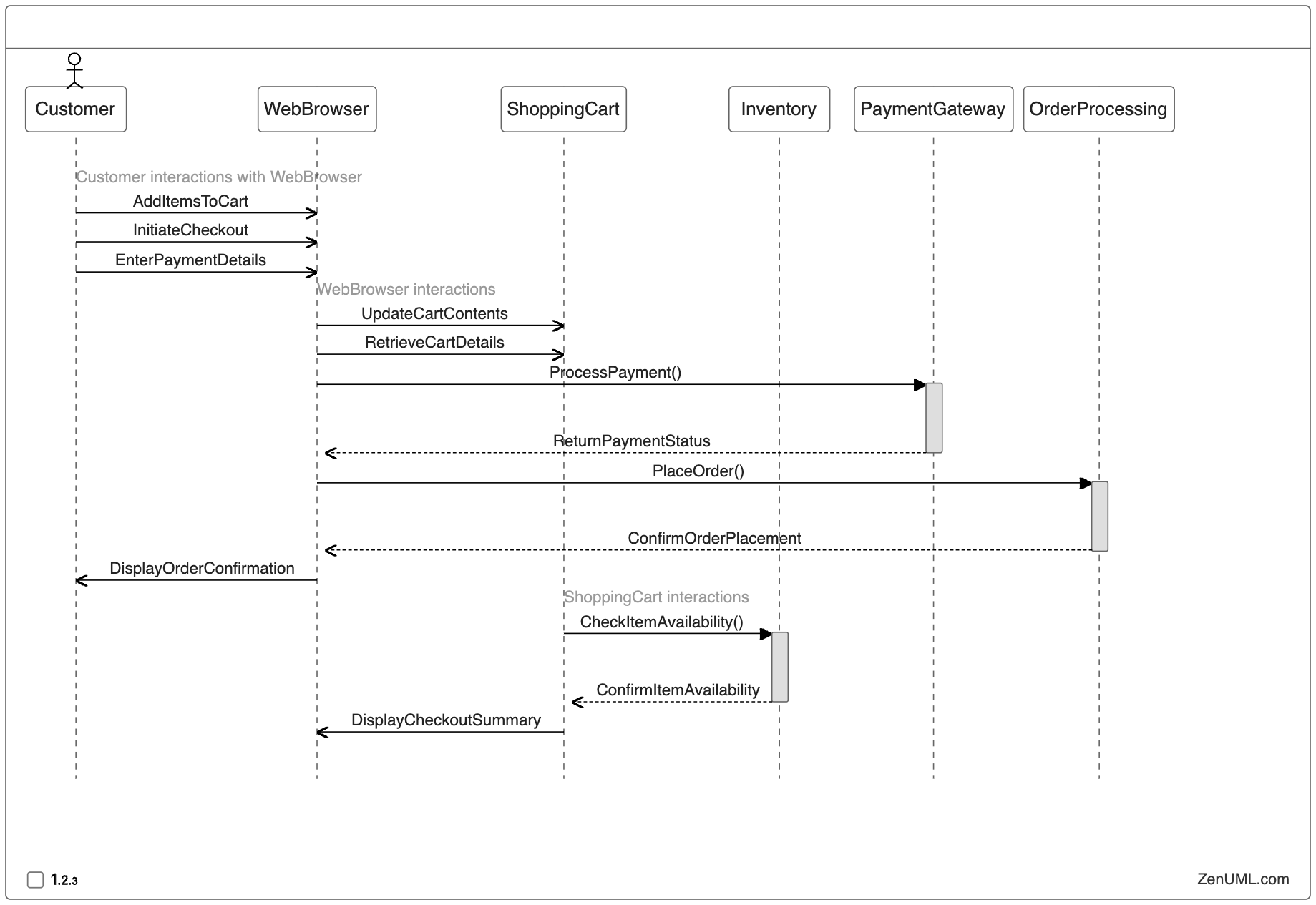
Based on this sequence diagram, we can design the following test cases:
- Successful Checkout: Verify that a customer can successfully complete the checkout process with valid items and payment details.
- Inventory Unavailability: Test the system's behavior when an item in the cart becomes unavailable during the checkout process.
- Payment Failure: Ensure that the system handles payment failures gracefully and provides the customer with appropriate error messages or retry options.
- Order Placement Failure: Validate the system's response when an issue occurs during the order placement process.
Example 3: Notification System
Suppose we have a notification system that sends alerts to users based on certain events. Here's a sequence diagram for the notification process:
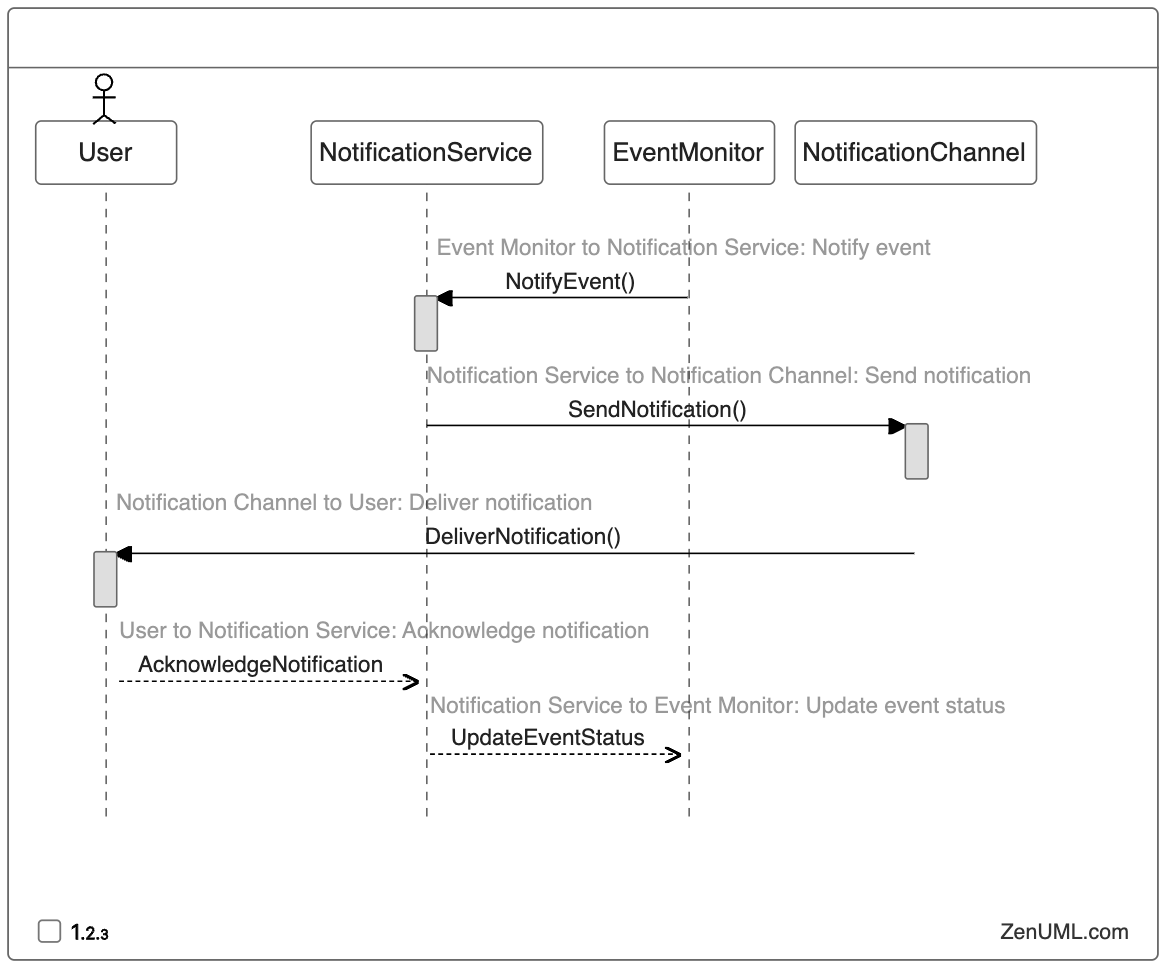
Based on this sequence diagram, we can design the following test cases:
- Successful Notification Delivery: Verify that the notification system can successfully deliver notifications to users through the configured channels.
- Failed Notification Delivery: Ensure that the system handles scenarios where the notification delivery fails and takes appropriate actions, such as retrying or escalating the issue.
- Notification Acknowledgment: Test the system's ability to update the event status when a user acknowledges the received notification.
- Notification Throttling: Validate that the system can handle a large volume of events and notifications without affecting the overall performance.
Conclusion
Sequence diagrams are a powerful tool for enhancing test case design and improving the overall quality of software systems. By leveraging sequence diagrams, testers can gain a deeper understanding of system behavior, identify edge cases, and design more comprehensive test cases. As software systems become increasingly complex, the use of sequence diagrams in test case design will continue to play a crucial role in ensuring the reliability and robustness of these systems.
We encourage you to explore the use of sequence diagrams in your own testing practices and share your experiences and insights in the comments below. Let's continue to strengthen the role of sequence diagrams in the pursuit of software excellence.
Try ZenUML now!
Zenuml detailed feature roadmap available here.