Introduction
Code reviews are an essential part of the software development process, ensuring codebase quality, identifying potential issues, and fostering collaboration among team members. However, communicating complex code structures and interactions during reviews can be challenging, often leading to lengthy discussions and potential misunderstandings. In this blog post, we'll explore how incorporating sequence diagrams can revolutionize your code review process, making it more efficient, effective, and insightful.
According to a study by the Software Engineering Institute, code reviews can detect up to 60% of software defects, highlighting their importance in the overall software development lifecycle. [1] However, the traditional approach of simply sharing code snippets and discussing them can be time-consuming and may not always provide the necessary context for a thorough review.
This is where sequence diagrams come into play. Sequence diagrams are a type of Unified Modeling Language (UML) diagram that visually represent the interactions between different objects or components within a system, showing the sequence of messages exchanged. By incorporating sequence diagrams into your code review process, you can effectively communicate the flow of control and data, making it easier for reviewers to understand the code and identify potential issues.
The Benefits of Using Sequence Diagrams in Code Reviews
-
Enhanced Visualization: Sequence diagrams provide a clear and concise visual representation of the code's structure and behavior, making it easier for reviewers to comprehend complex interactions and data flows. This can be particularly helpful when dealing with legacy code or unfamiliar systems.
-
Improved Communication: By presenting the code's functionality through sequence diagrams, reviewers can more effectively communicate their understanding, feedback, and suggestions, leading to more productive discussions and faster issue resolution.
-
Deeper Insights: Sequence diagrams can reveal subtle dependencies, race conditions, or potential bottlenecks that may not be immediately evident from the code alone. This can help identify hidden issues and ensure a more thorough code review.
-
Collaborative Exploration: Sequence diagrams can serve as a shared visual reference, enabling reviewers to collaboratively explore and discuss the code, fostering a deeper understanding and facilitating the decision-making process.
-
Knowledge Sharing: By creating and documenting sequence diagrams as part of the code review process, the team can build a valuable knowledge base that can be referenced in the future, easing the onboarding of new team members and facilitating knowledge transfer.
Incorporating Sequence Diagrams into the Code Review Process
To effectively integrate sequence diagrams into your code review process, follow these steps:
-
Identify Key Interactions: When preparing for a code review, take the time to identify the critical interactions, data flows, and control logic within the code that would benefit from a visual representation.
-
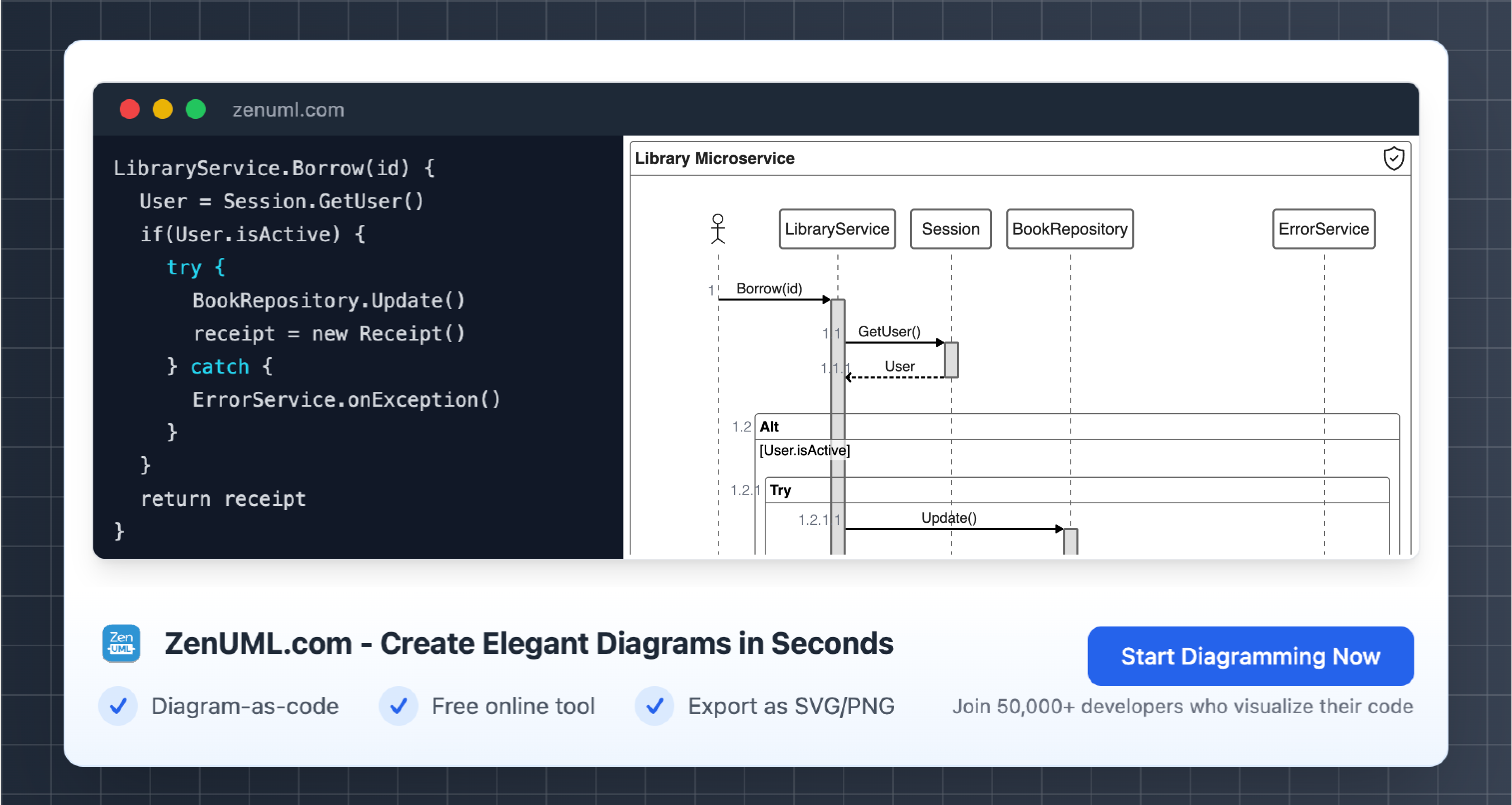
Create Sequence Diagrams: Use a tool like ZenUML, a markdown-based diagramming and charting tool, to create sequence diagrams that accurately capture the identified interactions. ZenUML's easy-to-use syntax and integration with various platforms make it a popular choice for incorporating sequence diagrams into your workflow.
Here's an example of a sequence diagram created with ZenUML:
-
Include Sequence Diagrams in the Review: When submitting the code for review, include the relevant sequence diagrams alongside the code changes. This will provide reviewers with a clear visual context, enabling them to better understand the code's behavior and identify potential issues.
-
Facilitate Discussion: During the code review, use the sequence diagrams as a starting point for discussion. Encourage reviewers to provide feedback, ask questions, and suggest improvements based on their understanding of the diagrams.
-
Iterate and Refine: Based on the feedback received, update the sequence diagrams to reflect any changes or clarifications. This iterative process ensures that the diagrams remain accurate and serve as a reliable reference for the team.
Practical Examples of Sequence Diagrams in Code Reviews
To illustrate the practical application of sequence diagrams in code reviews, let's consider a few examples.
Example 1: Web Application Authentication Workflow
Suppose you're reviewing the code for a web application's authentication workflow. A sequence diagram can help visualize the interactions between the client, web server, and authentication server, making it easier to identify potential security vulnerabilities or inefficiencies.
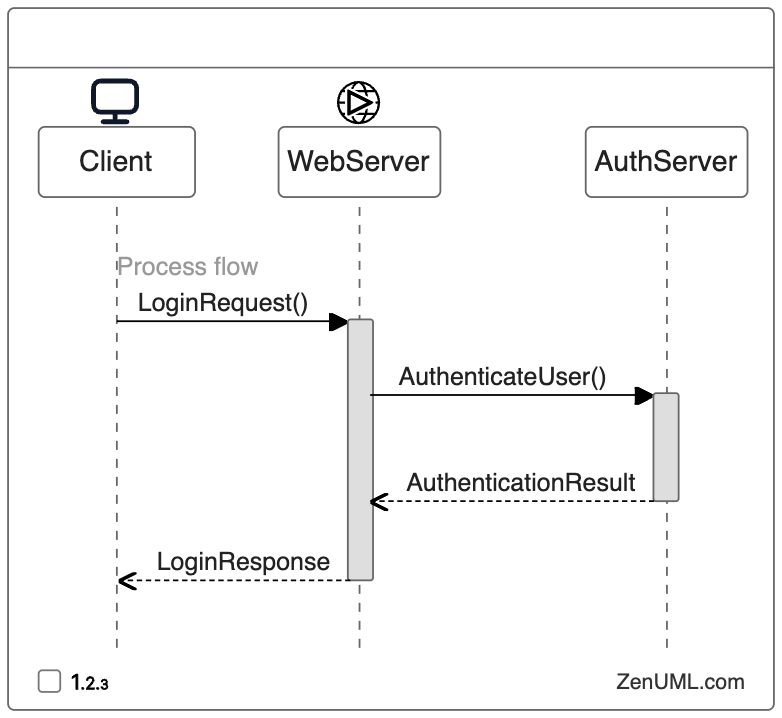
By examining this sequence diagram, reviewers can quickly understand the flow of the authentication process, identify any missing or incorrect steps, and suggest improvements to enhance the overall security and reliability of the system.
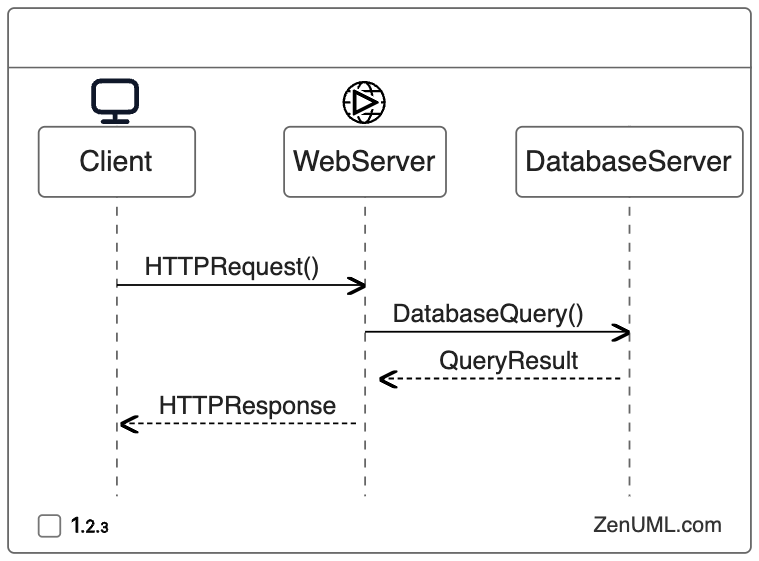
Example 2: Asynchronous Message Processing
In a microservices architecture, where services communicate asynchronously through message queues, a sequence diagram can help reviewers understand the flow of data and identify potential bottlenecks or race conditions.
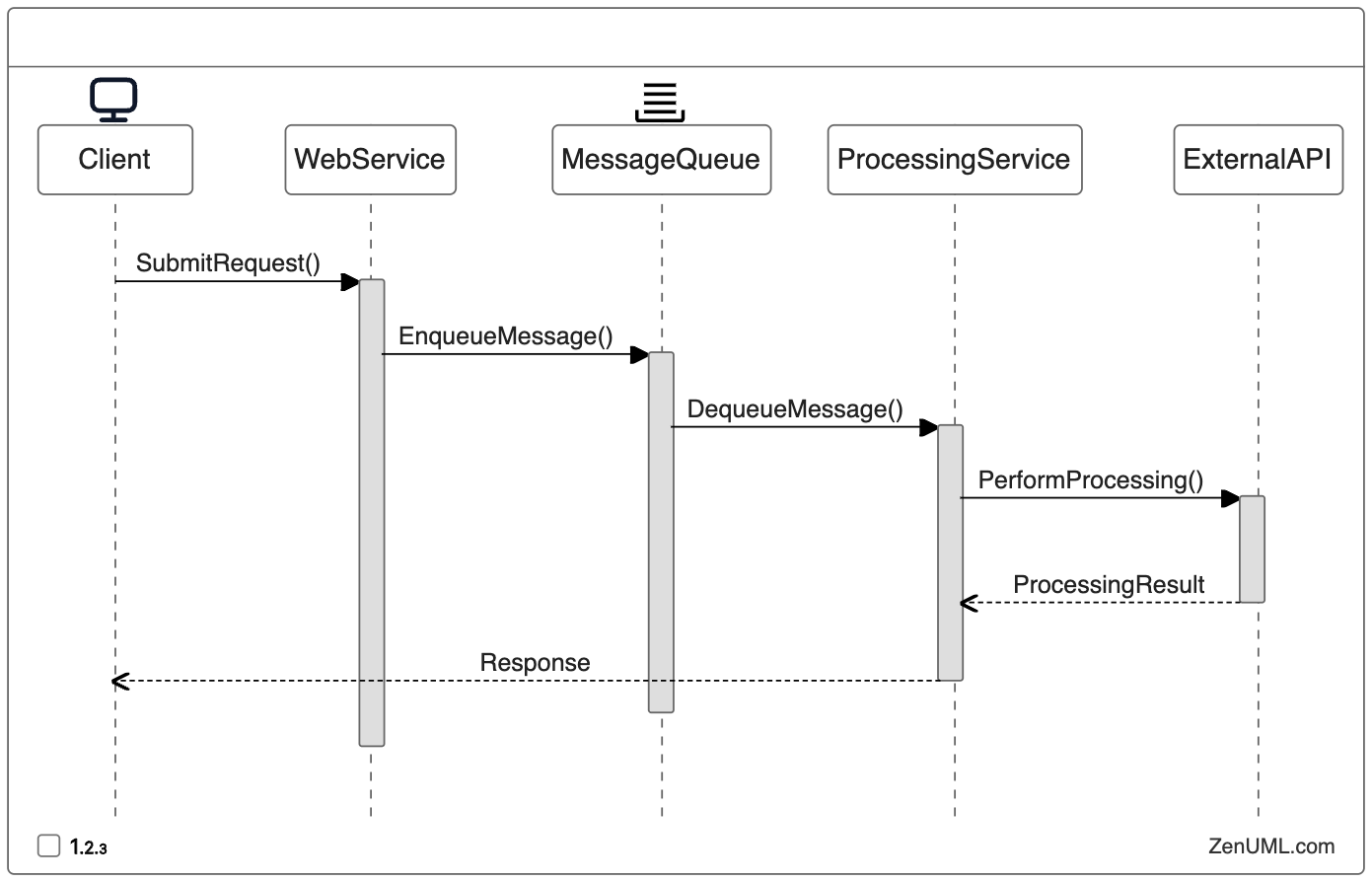
By visualizing the asynchronous message processing flow, reviewers can assess the reliability of the system, identify potential issues with message handling, and suggest optimizations to improve the overall performance and scalability.
Example 3: Complex API Interactions
When reviewing the code for a complex API with multiple endpoints and interdependent functionalities, a sequence diagram can help reviewers understand the interactions between the client, API, and related services.
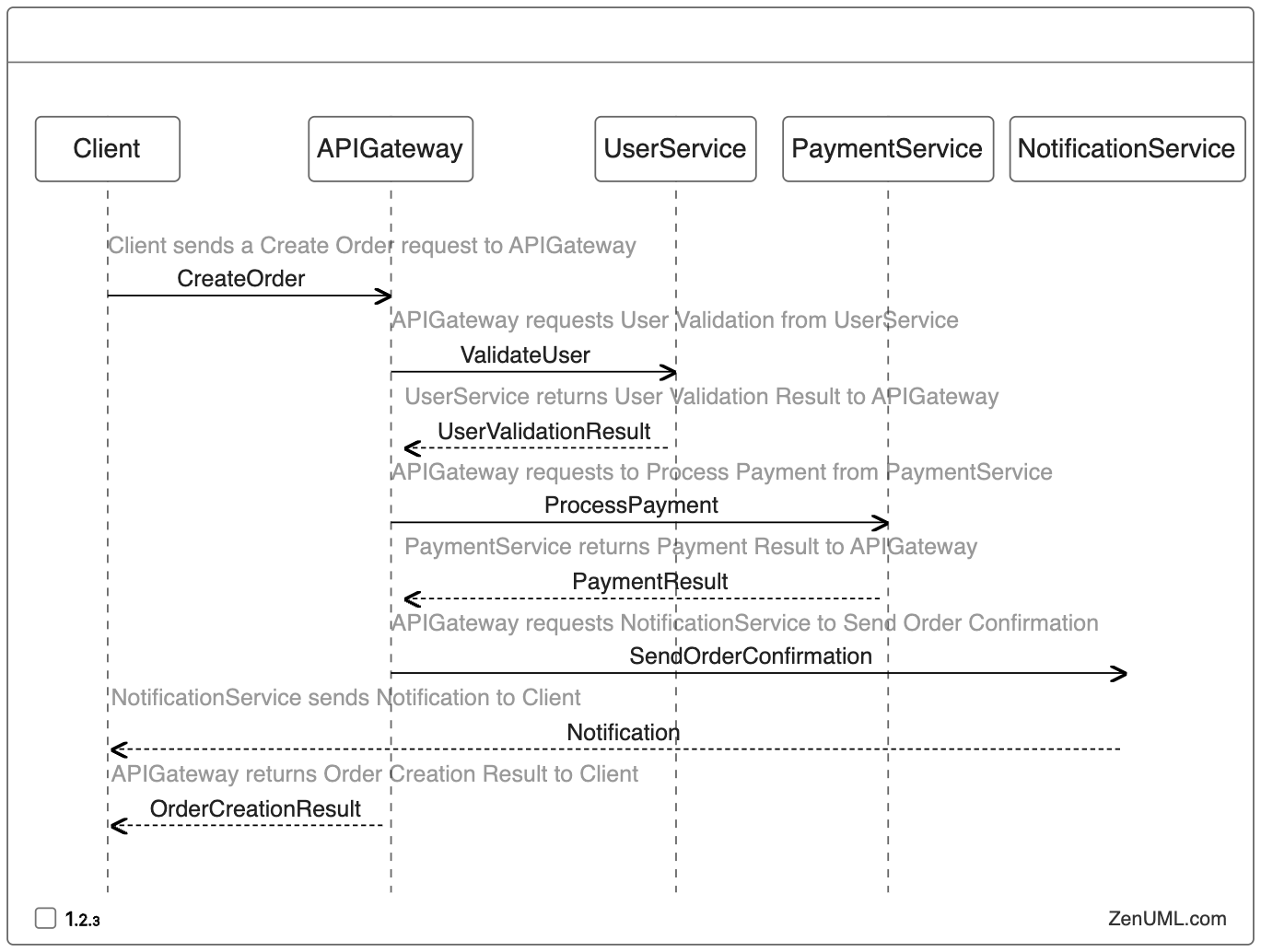
By examining this sequence diagram, reviewers can easily identify the flow of control and data, spot potential integration issues, and suggest improvements to the API's design and error handling mechanisms.
Conclusion
Incorporating sequence diagrams into your code review process can significantly enhance the effectiveness and efficiency of your team's collaboration. By providing a visual representation of the code's structure and behavior, sequence diagrams help reviewers better understand the system, identify potential issues, and communicate their feedback more effectively.
As you continue to refine your code review practices, consider integrating sequence diagrams as a valuable tool to streamline the process and foster a deeper understanding of the codebase. Remember, the key to success lies in the collaborative exploration of the code, and sequence diagrams can be a powerful catalyst in this journey.
We encourage you to try incorporating sequence diagrams into your next code review and experience the benefits firsthand. Don't hesitate to share your experiences and insights in the comments below. Together, we can continue to evolve and improve the way we approach code reviews, ensuring the delivery of high-quality software.
Try ZenUML now!
Zenuml detailed feature roadmap available here.