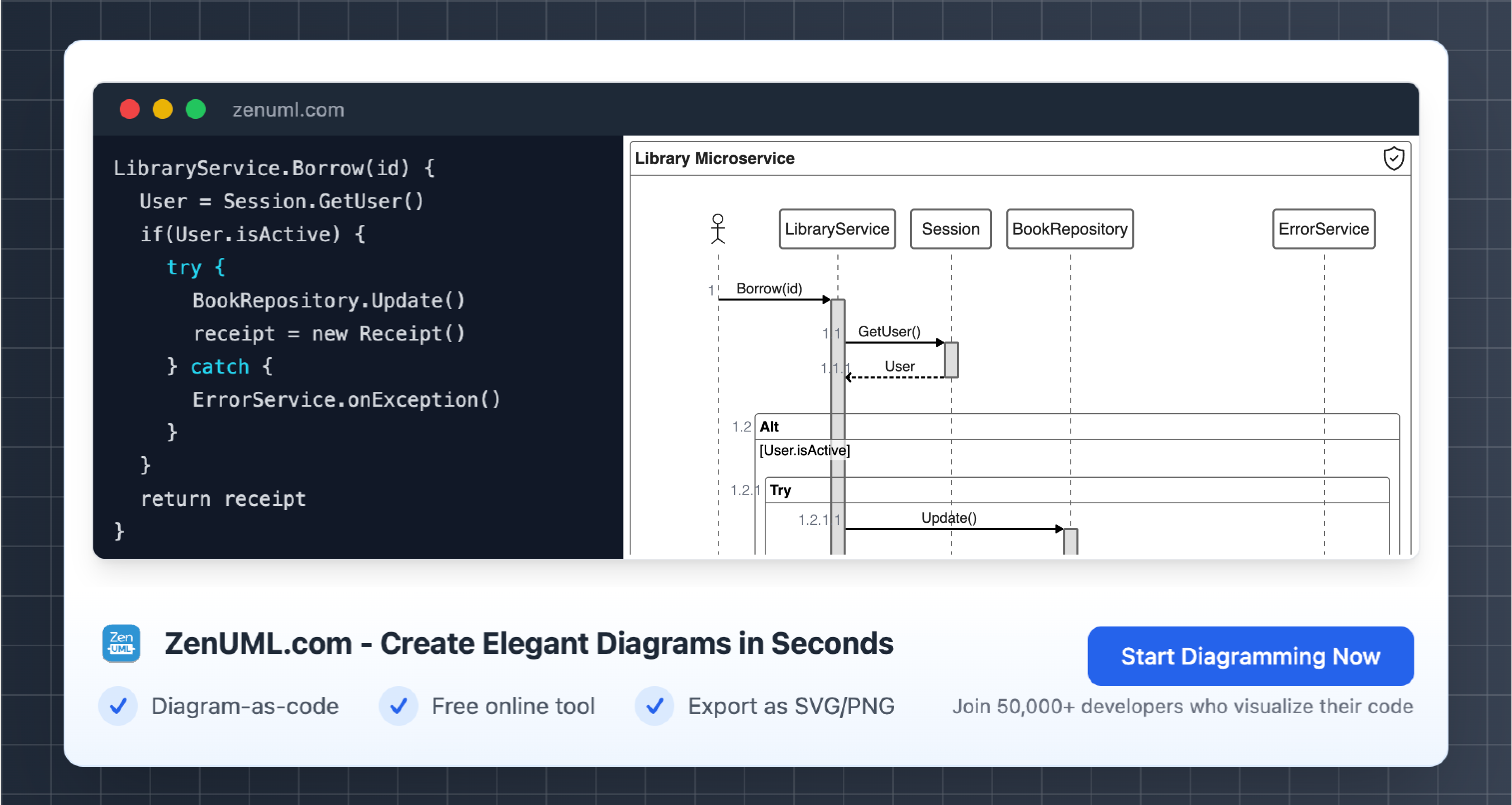
Introduction
Blockchain technology has revolutionized the way we think about digital transactions and data management. As the adoption of blockchain continues to grow, it's become increasingly important to have a clear understanding of the processes and interactions involved in blockchain-based transactions. One powerful tool for visualizing and understanding these complex processes is the sequence diagram.
Sequence diagrams are a type of UML (Unified Modeling Language) diagram that illustrate the flow of messages and interactions between different entities or objects over time. In the context of blockchain, sequence diagrams can be used to model the various steps and interactions involved in a blockchain transaction, from the initial request to the final confirmation and validation.
In this blog post, we'll explore the use of sequence diagrams for modeling blockchain transactions, providing practical examples and step-by-step explanations. We'll also introduce the ZenUML sequence diagram, a popular open-source tool for creating these diagrams in a simple, text-based format.
The Importance of Sequence Diagrams in Blockchain
Blockchain technology is built on a decentralized, distributed ledger that records transactions across a network of participating nodes. This complex system involves multiple parties, each with their own roles and responsibilities, making it challenging to visualize and understand the entire transaction process.
Sequence diagrams play a crucial role in this context by:
-
Enhancing Understanding: Sequence diagrams provide a clear and concise representation of the sequence of events and interactions involved in a blockchain transaction. This helps developers, stakeholders, and even non-technical users to better understand the underlying processes and identify potential bottlenecks or areas for improvement.
-
Facilitating Communication: By visualizing the transaction flow, sequence diagrams facilitate communication and collaboration among different teams, such as developers, designers, and business analysts, who may have varying levels of technical expertise.
-
Identifying Potential Issues: Carefully analyzing sequence diagrams can help identify potential issues or vulnerabilities in the blockchain transaction process, allowing developers to address them before they become problematic.
-
Documenting Blockchain Architectures: Sequence diagrams can be used to document the architecture and design of a blockchain-based system, serving as a valuable resource for future reference and maintenance.
Modeling Blockchain Transactions with Sequence Diagrams
To demonstrate the use of sequence diagrams in the context of blockchain transactions, let's consider a common scenario: a user initiating a cryptocurrency transaction on a blockchain network.
Step 1: Initiating the Transaction
The sequence diagram begins with the user initiating a transaction on their blockchain wallet or application. Here's an example using ZenUML:
// Define participants
@User "User"
@Wallet "Wallet"
@Node "Node"
@Blockchain "Blockchain"
// Sync Message from User to Wallet
"User" -> "Wallet".Initiate Transaction(){
// Wallet processes the transaction initiation
}
// Sync Message from Wallet to Node
"Wallet" -> "Node".Send Transaction Data(){
// Node processes the incoming transaction data
}
// Sync Message from Node to Blockchain
"Node" -> "Blockchain".Validate Transaction(){
// Blockchain validates the transaction
}
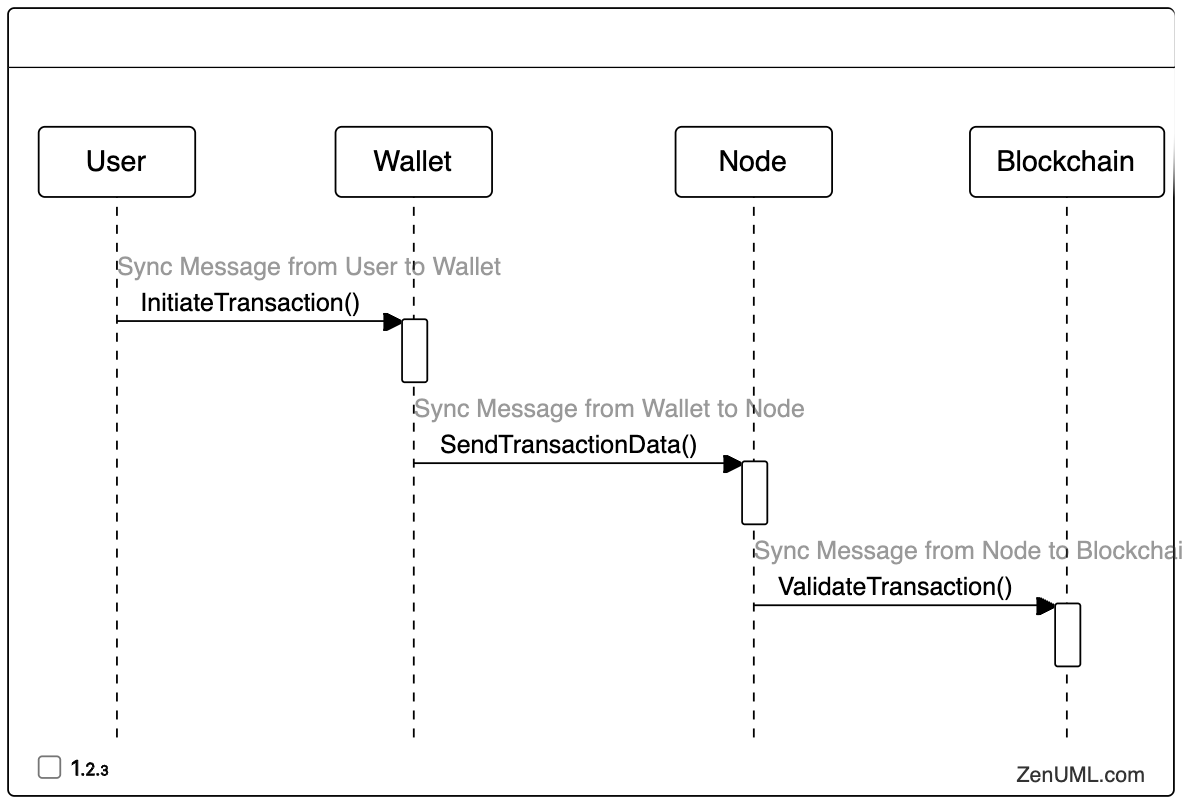
In this initial step, the user interacts with their blockchain wallet to initiate a transaction. The wallet then sends the transaction data to a node on the blockchain network for validation.
Step 2: Transaction Validation and Propagation
Once the node receives the transaction data, it proceeds to validate the transaction according to the blockchain's consensus rules. If the transaction is valid, the node will then propagate it to the rest of the network.
@User "User"
@Wallet "Wallet"
@Node "Node"
@Blockchain "Blockchain"
==Initiating the Transaction==
// Sync Message from User to Wallet
"User" -> "Wallet".InitiateTransaction(){
// Wallet processes the transaction initiation
}
// Sync Message from Wallet to Node
"Wallet" -> "Node".SendTransactionData(){
// Node processes the incoming transaction data
}
// Sync Message from Node to Blockchain
"Node" -> "Blockchain"."Validate Transaction"(){
// Blockchain validates the transaction
}
==Transaction Validation and Propagation==
// Validate Transaction
"Node" -> "Blockchain": Validate Transaction
// Transaction Validation Result
@return "Blockchain" -> "Node": Transaction Validation Result
// Propagate Transaction
"Node" -> "Blockchain": Propagate Transaction
// Transaction Propagation Confirmation
@return "Blockchain" -> "Node": Transaction Propagation Confirmation
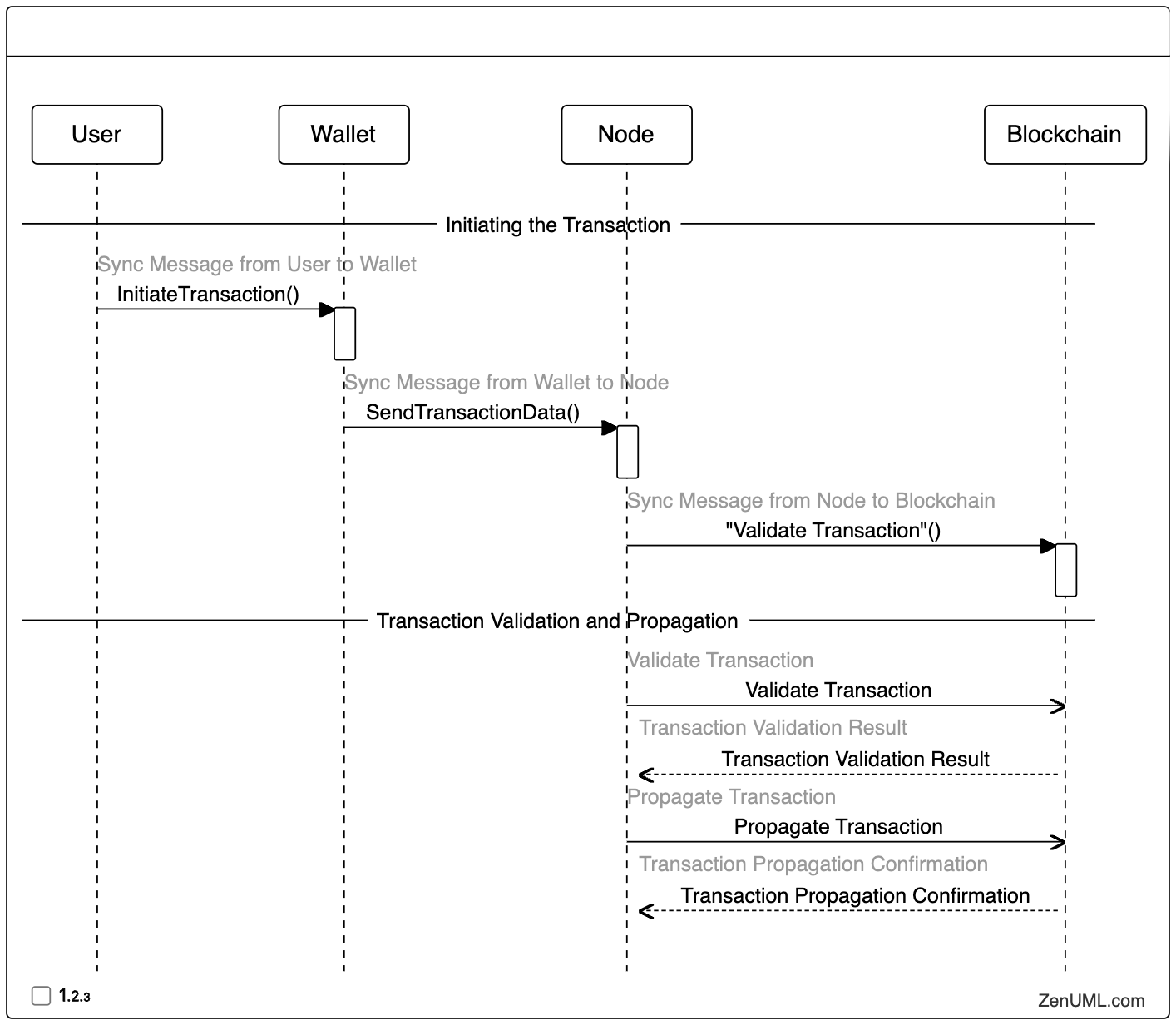
In this step, the node first sends the transaction data to the blockchain for validation. The blockchain then returns the validation result to the node. If the transaction is valid, the node will propagate the transaction to the rest of the network, and the blockchain will confirm the successful propagation.
Step 3: Transaction Inclusion in a Block
After the transaction has been propagated throughout the network, the next step is for the transaction to be included in a new block on the blockchain. This process typically involves miners or validators, who compete to add the next block to the chain.
// Define participants
@User "User"
@Wallet "Wallet"
@Node "Node"
@Miner "Miner"
@Blockchain "Blockchain"
// Broadcast New Block from Blockchain to Node
"Blockchain" -> "Node": Broadcast New Block
// Verify Block Validity from Node to Blockchain
"Node" -> "Blockchain": Verify Block Validity
// Block Confirmation from Blockchain to Node
"Blockchain" -> "Node": Block Confirmation
// Transaction Finalized from Node to User
"Node" -> "User": Transaction Finalized
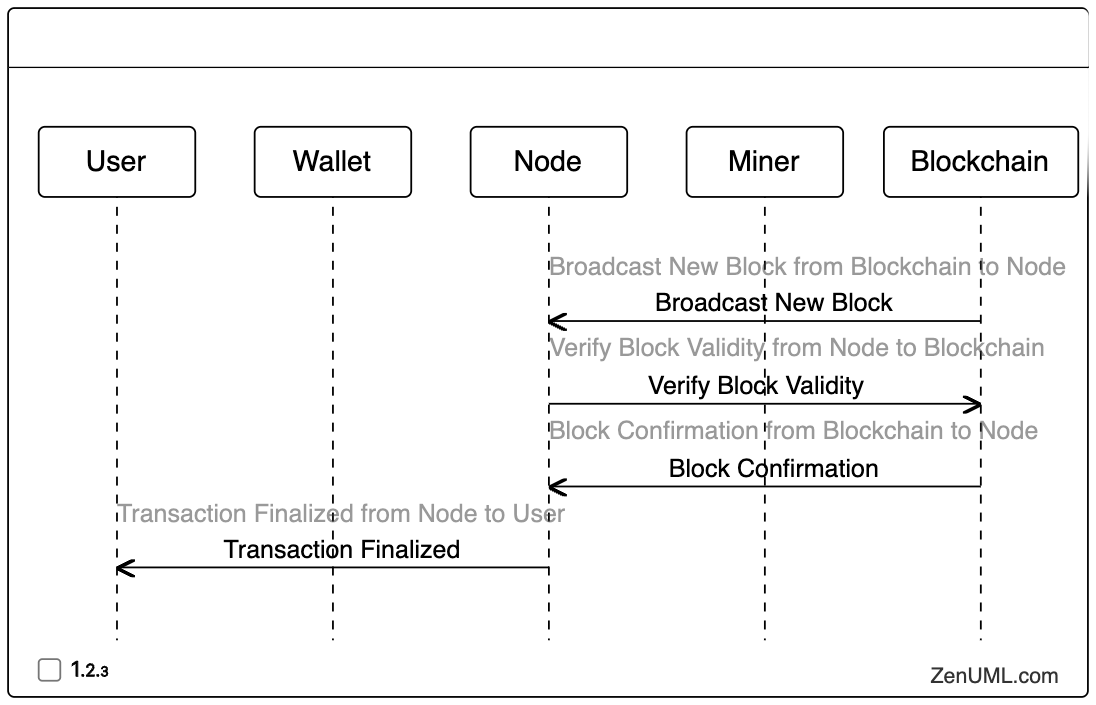
In this step, a miner or validator requests a new block template from the blockchain. The miner then adds the transaction to the block and submits it back to the blockchain, which confirms the successful inclusion of the transaction in the new block.
Step 4: Block Confirmation and Finalization
After the transaction has been included in a new block, the blockchain network must reach a consensus on the validity of the block. This process involves other nodes on the network verifying and confirming the block.
// Define participants
@Blockchain "Blockchain"
@Node "Node"
@User "User"
// Broadcast New Block from Blockchain to Node
"Blockchain" -> "Node"."Broadcast New Block"(){
// Verify Block Validity from Node to Blockchain
"Node" -> "Blockchain"."Verify Block Validity"(){
// Block Confirmation from Blockchain to Node
"Blockchain" -> "Node":"Block Confirmation"
}
}
// Transaction Finalized from Node to User
"Node" -> "User"."Transaction Finalized"
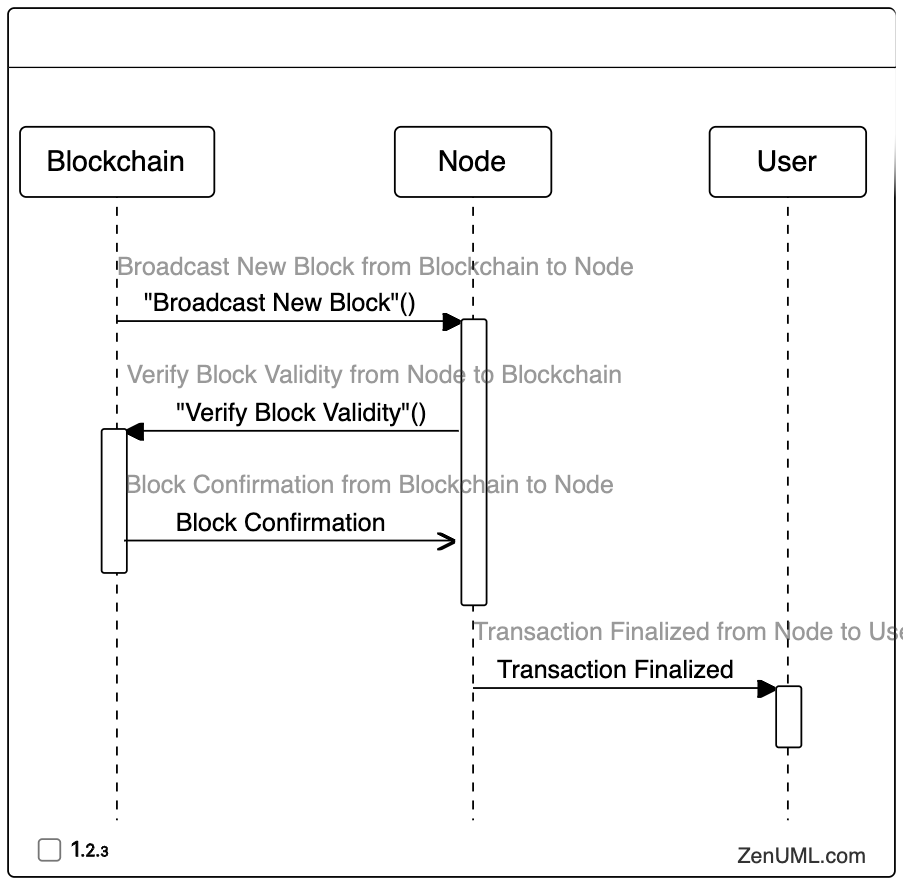
In this final step, the blockchain broadcasts the new block containing the transaction to the nodes on the network. The nodes then verify the validity of the block, and the blockchain confirms the successful verification. Finally, the node informs the user that the transaction has been finalized and added to the blockchain.
Conclusion
Sequence diagrams are a powerful tool for modeling and understanding blockchain transactions. By visualizing the various steps and interactions involved, sequence diagrams can help developers, stakeholders, and users better comprehend the complex processes underlying blockchain-based systems.
In this blog post, we've explored the importance of sequence diagrams in the context of blockchain and walked through a practical example of modeling a cryptocurrency transaction using the ZenUML sequence diagram tool. By leveraging sequence diagrams, blockchain teams can improve communication, identify potential issues, and document their architectural designs more effectively.
As the blockchain ecosystem continues to evolve, the use of sequence diagrams will become increasingly valuable in helping us navigate the complexities of this transformative technology. We encourage you to experiment with sequence diagrams and explore how they can enhance your understanding and development of blockchain-based applications.
We'd love to hear your thoughts and experiences with using sequence diagrams for blockchain modeling. Feel free to leave a comment below and share your insights with the community.
Try ZenUML now!
Zenuml detailed feature roadmap available here.