Introduction
In today's digital landscape, where security and accessibility are paramount, businesses must navigate the delicate balance between protecting their systems and providing seamless user experiences. One key tool in this endeavor is the use of sequence diagrams, which offer a powerful way to visualize and understand complex business processes. In this article, we will explore the application of sequence diagrams in the context of two-factor authentication (2FA), a widely adopted security measure that enhances the integrity of user authentication.
Two-factor authentication is a security protocol that requires users to provide two distinct forms of identification to access a system or account. This approach goes beyond the traditional username and password combination, adding an extra layer of security to prevent unauthorized access. Sequence diagrams provide a valuable means of modeling and documenting the interactions and sequences involved in the 2FA process, enabling businesses to streamline their security measures and optimize the user experience.
Sequence Diagram for Two-Factor Authentication
Let's dive into an example of a sequence diagram that illustrates the 2FA process. Using the ZenUML syntax, we can create an interactive and visually appealing diagram that showcases the various components and their interactions.
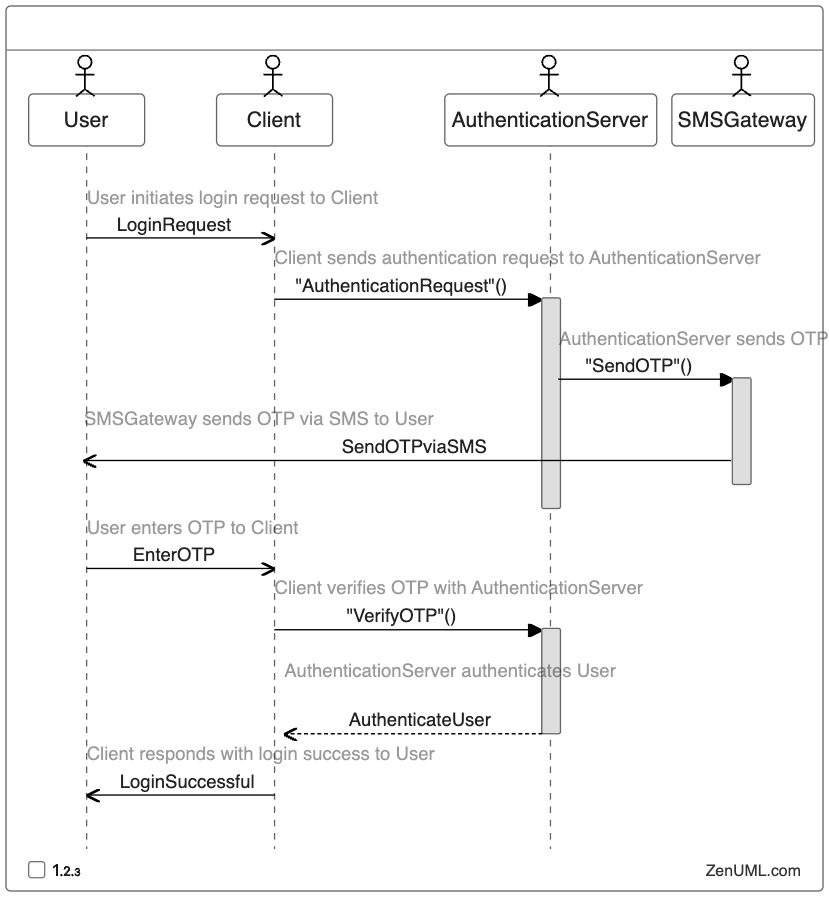
In this sequence diagram, we can see the step-by-step interactions between the user, the client application, the authentication server, and the SMS gateway during the two-factor authentication process.
- User Login Request: The user initiates a login request through the client application.
- Authentication Request: The client application forwards the authentication request to the authentication server.
- Send OTP: The authentication server sends a one-time password (OTP) to the SMS gateway, which in turn sends the OTP to the user's registered mobile device via SMS.
- Enter OTP: The user receives the OTP and enters it into the client application.
- Verify OTP: The client application sends the entered OTP to the authentication server for verification.
- Authenticate User: If the OTP is valid, the authentication server authenticates the user and sends a successful authentication response to the client application.
- Login Successful: The client application confirms the successful login to the user.
This sequence diagram provides a clear and comprehensive visualization of the 2FA process, allowing stakeholders to understand the flow of information and the interactions between the various components involved.
Benefits of Using Sequence Diagrams for Two-Factor Authentication
Incorporating sequence diagrams into the design and implementation of two-factor authentication systems offers several key benefits:
-
Process Visualization: Sequence diagrams provide a visual representation of the 2FA process, making it easier for stakeholders, developers, and security teams to understand the flow of information and the interactions between different components.
-
Requirement Gathering: By modeling the 2FA process using sequence diagrams, businesses can better identify and document the various requirements, including user interactions, server-side processes, and external integrations (such as the SMS gateway).
-
Implementation Guidance: The sequence diagram serves as a blueprint for the actual implementation of the 2FA system, guiding developers in understanding the expected behavior and ensuring the correct implementation of the process.
-
Documentation and Communication: Sequence diagrams can be used to document the 2FA process and facilitate communication between different teams (e.g., business analysts, developers, security experts) involved in the development and deployment of the system.
-
Troubleshooting and Maintenance: In the event of issues or the need for updates, the sequence diagram can be a valuable reference point, helping teams quickly understand the underlying process and make informed decisions about system modifications or enhancements.
-
Compliance and Auditing: Sequence diagrams can be used to demonstrate the security measures and processes in place, which is especially important for businesses operating in regulated industries or those that need to comply with specific security standards or guidelines.
By leveraging sequence diagrams, businesses can enhance the development, deployment, and ongoing management of their two-factor authentication systems, ultimately improving the overall security posture and user experience.
Key Considerations for Designing 2FA with Sequence Diagrams
When designing two-factor authentication systems using sequence diagrams, there are several key considerations to keep in mind:
-
User Experience: The sequence diagram should prioritize the user experience, ensuring a seamless and intuitive 2FA process that does not introduce unnecessary friction or complexity.
-
Security Measures: The diagram should clearly illustrate the security measures in place, such as the use of secure communication channels, encryption, and the handling of sensitive data (e.g., OTPs).
-
Error Handling: The sequence diagram should include well-defined error handling mechanisms, such as the handling of invalid OTPs, network failures, or other exceptional scenarios.
-
Scalability and Resilience: The 2FA process should be designed with scalability and resilience in mind, allowing the system to handle increasing user loads and withstand potential failures or disruptions.
-
Integration with Other Systems: If the 2FA process involves integration with external systems (e.g., SMS gateways, push notification services), the sequence diagram should capture these interactions and dependencies.
-
Compliance and Regulatory Requirements: Businesses operating in regulated industries may need to adhere to specific security standards or guidelines, which should be reflected in the sequence diagram.
-
Logging and Auditing: The 2FA process should incorporate robust logging and auditing mechanisms to enable monitoring, troubleshooting, and compliance reporting.
By carefully considering these key aspects during the design phase and incorporating them into the sequence diagram, businesses can ensure the development and implementation of a secure, scalable, and user-friendly two-factor authentication system.
Conclusion
In the ever-evolving landscape of digital security, the use of sequence diagrams in business process modeling has become an invaluable tool, particularly in the context of two-factor authentication. By visualizing the 2FA process and its underlying interactions, businesses can better understand, document, and optimize their security measures while enhancing the overall user experience.
As you continue to explore and implement two-factor authentication in your organization, I encourage you to leverage the power of sequence diagrams. These diagrams can serve as a foundational element in your security strategy, guiding your teams through the design, development, and deployment of a robust and user-friendly 2FA system.
I'd be delighted to hear your thoughts and experiences on the use of sequence diagrams in your business processes. Feel free to leave a comment below and share your insights with the community.
Try ZenUML now!
Zenuml detailed feature roadmap available here.