Introduction
Behavior-Driven Development (BDD) has become a popular approach in the software development industry, as it focuses on defining and validating the expected behavior of an application before diving into the implementation details. One powerful tool that can be seamlessly integrated into the BDD workflow is sequence diagrams. Sequence diagrams provide a visual representation of the interactions between different actors and components within a system, making it easier for both technical and non-technical stakeholders to understand and collaborate on the desired application behavior.
In this blog post, we will explore the synergy between BDD and sequence diagrams, and how you can leverage this combination to enhance your software development process. We'll dive into practical examples, using ZenUML sequence diagrams to illustrate the concepts, and demonstrate how this approach can improve communication, collaboration, and ultimately, the quality of your software.
Understanding BDD and Sequence Diagrams
Behavior-Driven Development is a software development methodology that emphasizes the collaboration between business stakeholders, developers, and quality assurance (QA) teams. The core idea behind BDD is to define the expected behavior of the system using natural language, which is then translated into automated tests. This approach helps to ensure that the software being developed aligns with the business requirements and user expectations.
Sequence diagrams, on the other hand, are a type of UML (Unified Modeling Language) diagram that visually represents the flow of messages and interactions between different objects or components within a system. These diagrams provide a clear and concise way to communicate the behavioral aspects of a system, making them an invaluable tool in the BDD process.
Integrating BDD and Sequence Diagrams
The integration of BDD and sequence diagrams can be a powerful combination, as it allows you to bridge the gap between business requirements and technical implementation. Here's how you can leverage this synergy:
1. Defining Scenarios with Sequence Diagrams
One of the key aspects of BDD is the use of user stories and scenarios to define the expected behavior of the system. Sequence diagrams can be used to visualize these scenarios, making it easier for all stakeholders to understand and validate the proposed interactions.
Let's consider a simple example of a user logging into an e-commerce website. Here's how you can use a sequence diagram to define the scenario:
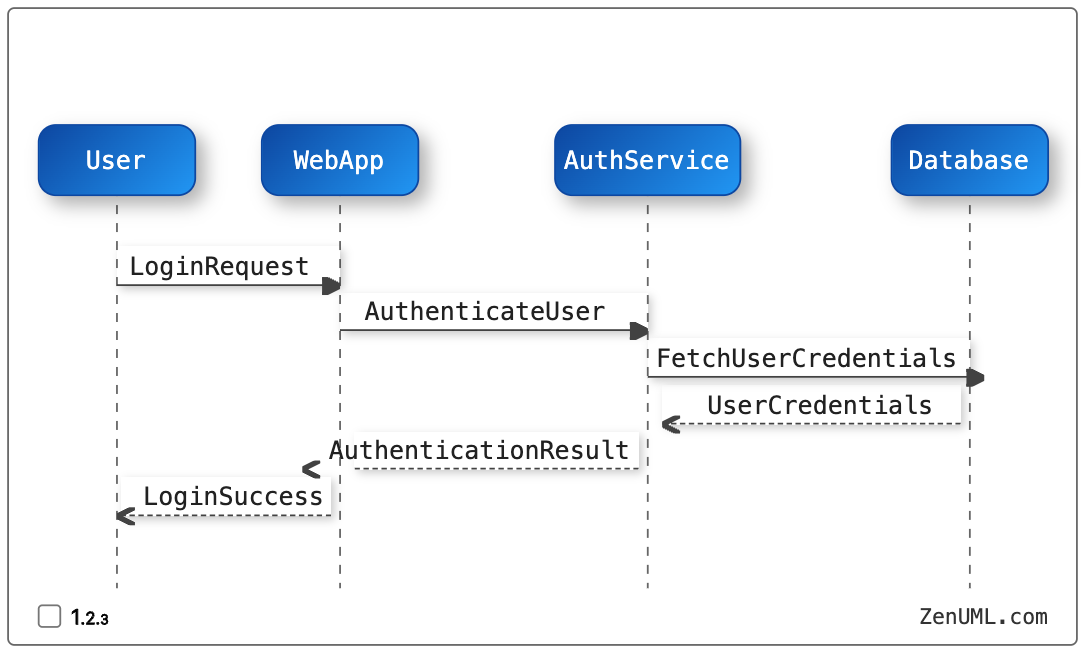
By using a sequence diagram, you can clearly depict the flow of interactions between the user, the web application, the authentication service, and the database. This visual representation helps to ensure that all stakeholders have a shared understanding of the expected behavior, which can then be translated into executable tests.
2. Refining and Validating Scenarios
As you progress through the BDD process, sequence diagrams can be used to refine and validate the scenarios. This includes identifying edge cases, potential failure points, and areas for optimization. By continuously updating the sequence diagrams, you can ensure that the defined scenarios accurately reflect the desired system behavior.
For example, let's consider an additional scenario where the user enters incorrect login credentials. We can update the sequence diagram to include this case:
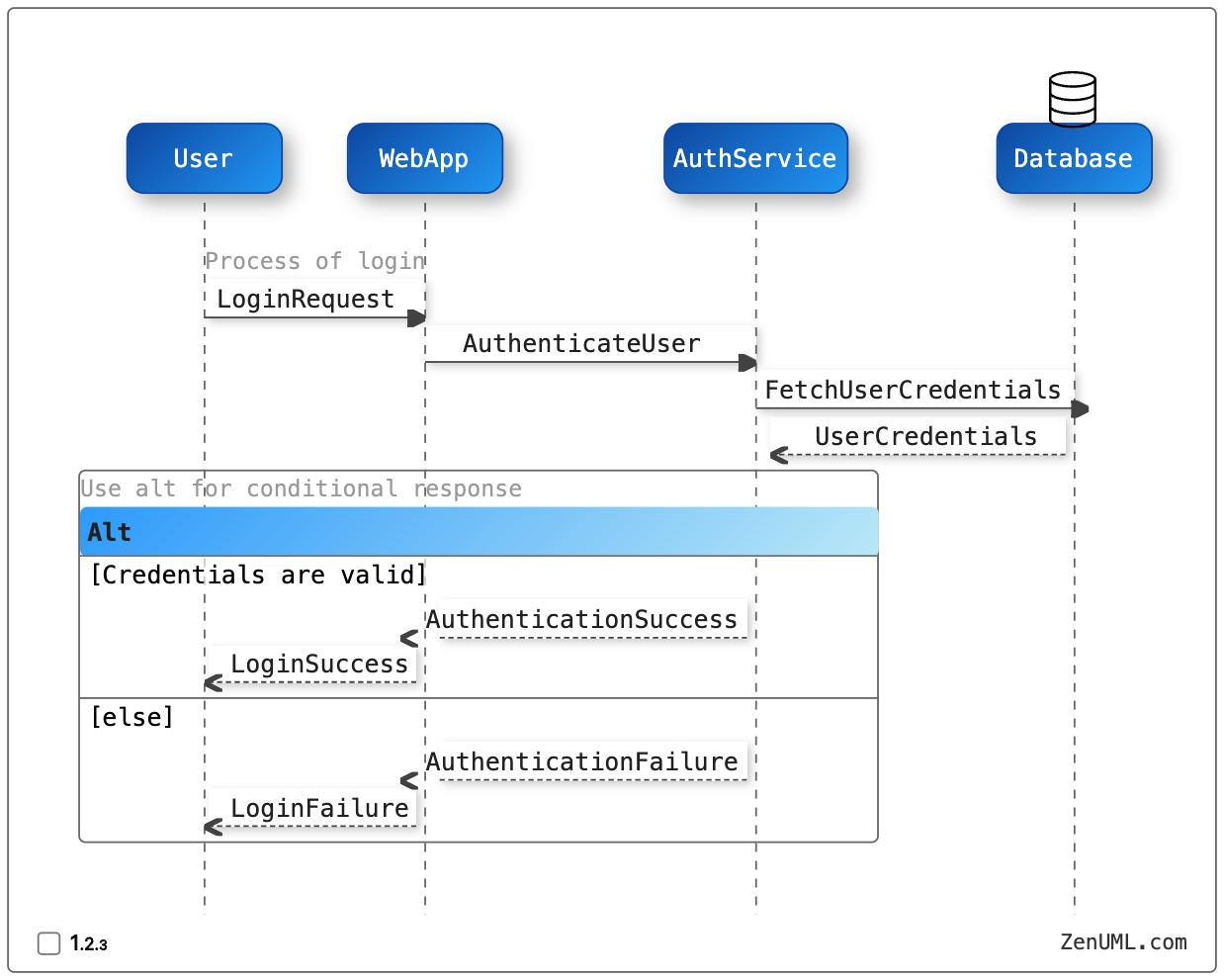
By incorporating this edge case into the sequence diagram, you can ensure that the defined scenarios cover all the necessary behavior, and that the corresponding tests accurately reflect the system requirements.
3. Facilitating Collaboration and Communication
Sequence diagrams can serve as a powerful communication tool, helping to bridge the gap between business stakeholders and technical teams. By providing a visual representation of the system interactions, sequence diagrams can facilitate discussions, elicit feedback, and ensure that everyone involved has a shared understanding of the expected behavior.
This collaborative approach can be particularly beneficial during the BDD process, where different stakeholders (e.g., product owners, developers, QA engineers) need to work together to define and validate the application's behavior. Sequence diagrams can be used as a common language to discuss and refine the scenarios, fostering better communication and collaboration among the team.
4. Guiding Implementation and Testing
Once the scenarios have been defined and validated using sequence diagrams, the next step is to translate them into executable tests. This is where the sequence diagrams can provide valuable guidance for the implementation and testing phases.
Developers can use the sequence diagrams to understand the expected interactions between the different components of the system, and then implement the corresponding functionality. Similarly, QA engineers can use the sequence diagrams to design and execute their test cases, ensuring that the system behaves as expected.
By aligning the implementation and testing efforts with the sequence diagrams, you can ensure that the software being developed matches the defined scenarios and business requirements, reducing the risk of costly rework and improving the overall quality of the application.
Practical Example: Implementing a Shopping Cart
To illustrate the practical application of BDD and sequence diagrams, let's consider a common use case: implementing a shopping cart functionality in an e-commerce application.
Defining the Scenario
Suppose we have the following user story:
"As a customer, I want to be able to add items to my shopping cart, update the quantities, and remove items, so that I can easily manage my purchases before checkout."
We can then define the following scenarios using a sequence diagram:
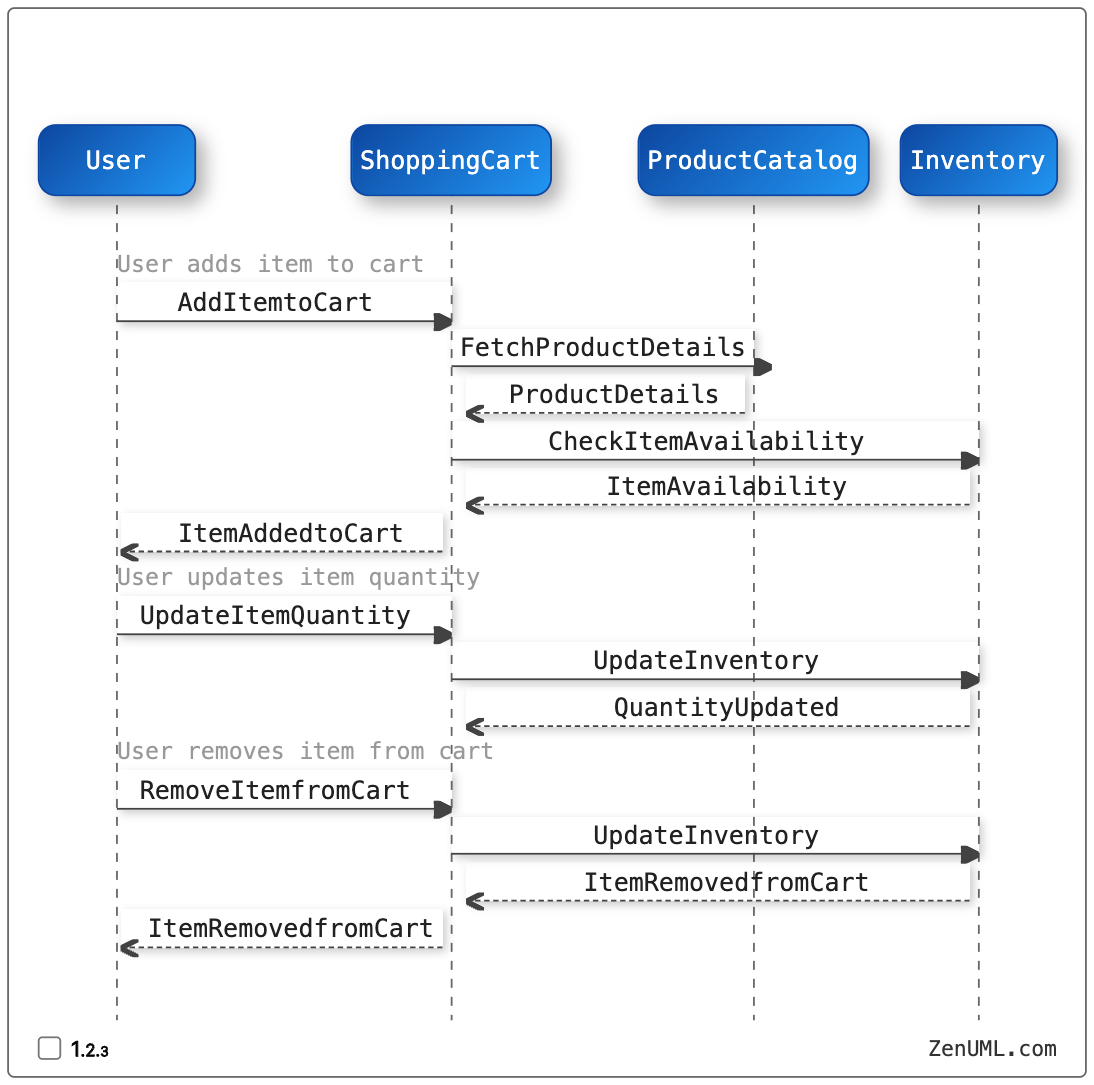
This sequence diagram depicts the interactions between the user, the shopping cart, the product catalog, and the inventory system. It covers the key scenarios of adding an item to the cart, updating the quantity, and removing an item from the cart.
Implementing the Scenarios
With the sequence diagram as a guide, the development team can now implement the shopping cart functionality, ensuring that it aligns with the defined scenarios.
For example, the "Add Item to Cart" scenario would involve the following steps:
- The user initiates an "Add to Cart" action in the user interface.
- The shopping cart module retrieves the product details from the product catalog.
- The shopping cart module checks the item availability in the inventory system.
- If the item is available, the shopping cart updates its internal state and notifies the user of the successful addition.
Similarly, the "Update Item Quantity" and "Remove Item from Cart" scenarios would be implemented based on the corresponding interactions shown in the sequence diagram.
Testing the Scenarios
The sequence diagram can also serve as a blueprint for the test cases. QA engineers can use the diagram to identify the key interactions and design test cases that cover the expected behavior.
For example, the "Add Item to Cart" scenario can be tested by:
- Verifying that the user can successfully add an item to the cart.
- Checking that the product details are correctly fetched from the product catalog.
- Ensuring that the item availability is correctly checked in the inventory system.
- Validating that the shopping cart's internal state is updated correctly, and the user is notified of the successful addition.
By aligning the test cases with the sequence diagram, the QA team can ensure that the implemented functionality matches the defined scenarios and the overall system behaves as expected.
Conclusion
Behavior-Driven Development and sequence diagrams are a powerful combination that can significantly improve the software development process. By integrating these techniques, you can enhance communication, collaboration, and the overall quality of your software.
Sequence diagrams provide a visual representation of the expected system behavior, which can then be use
Try ZenUML now!
Zenuml detailed feature roadmap available here.