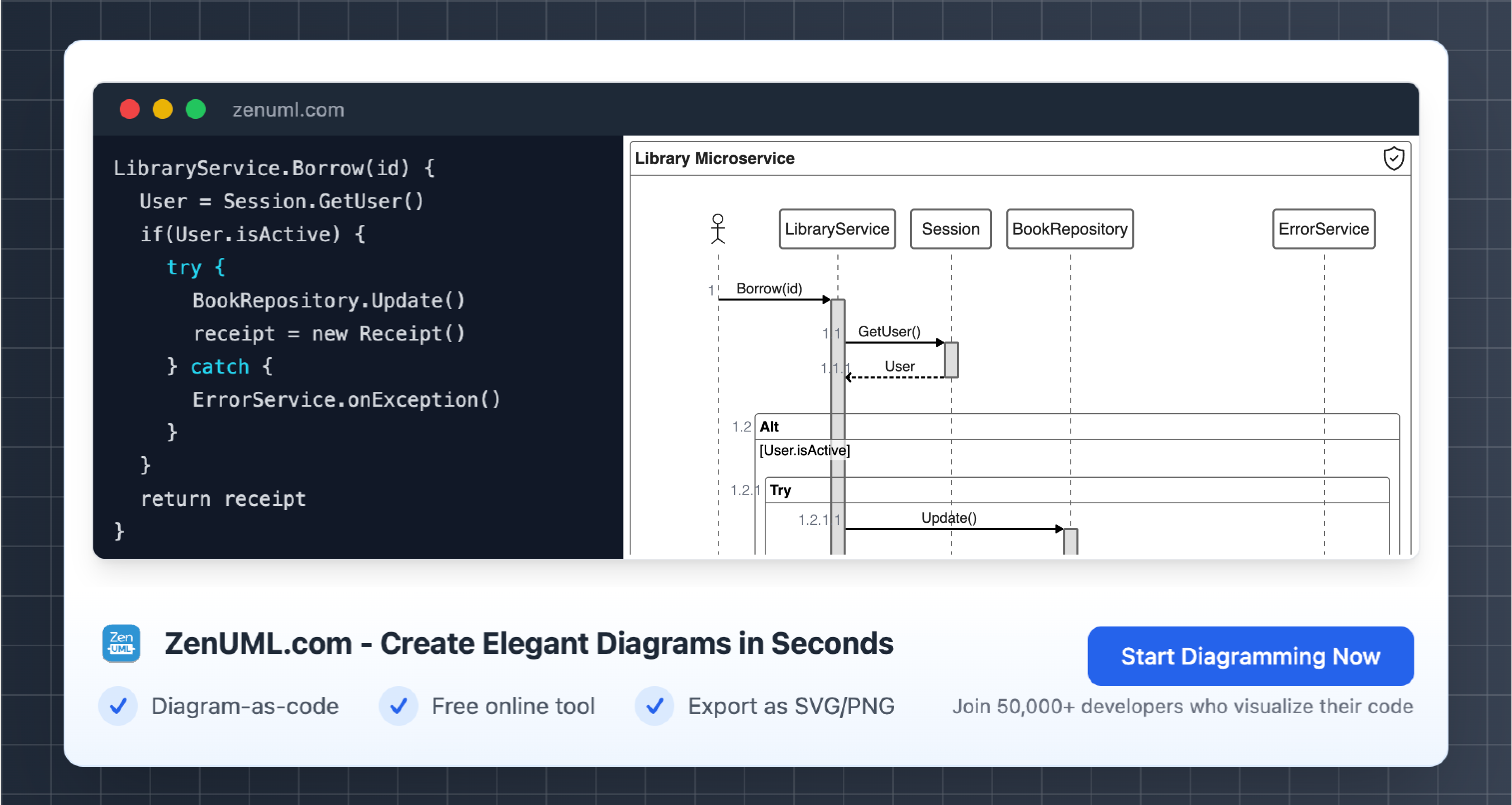
Introduction
In the dynamic and ever-evolving world of game development, streamlining workflows and ensuring efficient communication among team members is paramount. One powerful tool that has gained traction in this industry is the use of sequence diagrams. Sequence diagrams, a type of Unified Modeling Language (UML) diagram, provide a visual representation of the interactions and message exchanges between various entities within a system.
For game developers, sequence diagrams can serve as a game-changer, enabling them to better understand, communicate, and optimize their game's architecture and functionality. By leveraging the power of sequence diagrams, developers can improve collaboration, identify potential bottlenecks, and enhance the overall quality of their game projects.
In this blog post, we will delve into the world of sequence diagrams and explore how they can be effectively utilized in game development workflows. We'll discuss the benefits of incorporating sequence diagrams, provide practical examples, and demonstrate how to create them using the popular ZenUML diagramming syntax.
The Benefits of Sequence Diagrams in Game Development
-
Improved Communication and Collaboration: Sequence diagrams offer a common language for the entire development team, allowing them to visualize and understand the interactions between different components and systems within the game. This shared understanding fosters better communication, reduces misunderstandings, and facilitates more effective collaboration among team members.
-
Enhanced System Modeling and Design: By creating sequence diagrams, developers can model the dynamic behavior of their game's systems, including the flow of messages, the timing of interactions, and the responsibilities of each entity. This modeling process helps identify potential issues, optimize design decisions, and ensure the overall coherence and scalability of the game's architecture.
-
Debugging and Troubleshooting: Sequence diagrams can be invaluable during the debugging and troubleshooting phases of game development. By providing a visual representation of the interactions between different components, developers can more easily identify and resolve issues, such as deadlocks, race conditions, or unexpected message sequences.
-
Onboarding and Knowledge Sharing: Sequence diagrams can serve as valuable resources for onboarding new team members or sharing knowledge with stakeholders. By clearly documenting the game's system interactions, these diagrams can facilitate a faster understanding of the codebase, reduce the learning curve, and enable more effective knowledge transfer among team members.
-
Optimization and Performance Monitoring: Sequence diagrams can help developers identify potential performance bottlenecks or inefficient message flows within their game's systems. By visualizing the interactions and message exchanges, developers can optimize the game's architecture, streamline communication pathways, and improve overall system performance.
Practical Examples of Sequence Diagrams in Game Development
To illustrate the practical applications of sequence diagrams in game development, let's consider the following examples:
Example 1: Player Authentication and Matchmaking
Consider a multiplayer game where players need to authenticate and be matched with opponents. Here's a sequence diagram that outlines the interactions involved:
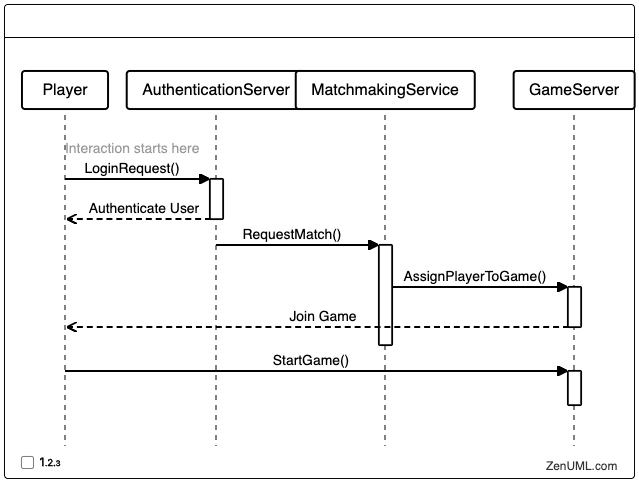
In this example, the sequence diagram demonstrates the flow of interactions between the player, the authentication server, the matchmaking service, and the game server. It clearly shows the message exchanges and the order in which they occur, helping developers understand and optimize the player authentication and matchmaking process.
Example 2: In-Game Item Purchase
Let's consider the flow of interactions when a player purchases an in-game item:
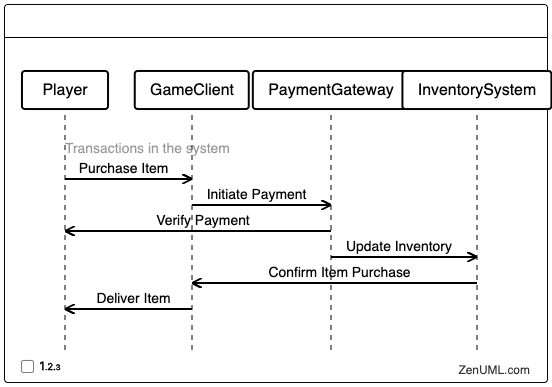
This sequence diagram illustrates the interactions between the player, the game client, the payment gateway, and the inventory system during an in-game item purchase. It helps developers understand the flow of information, identify potential bottlenecks, and ensure the integrity of the payment and inventory management processes.
Example 3: Game Entity Interaction
In a more complex game scenario, let's consider the interactions between various game entities, such as a player, an enemy, and a projectile:
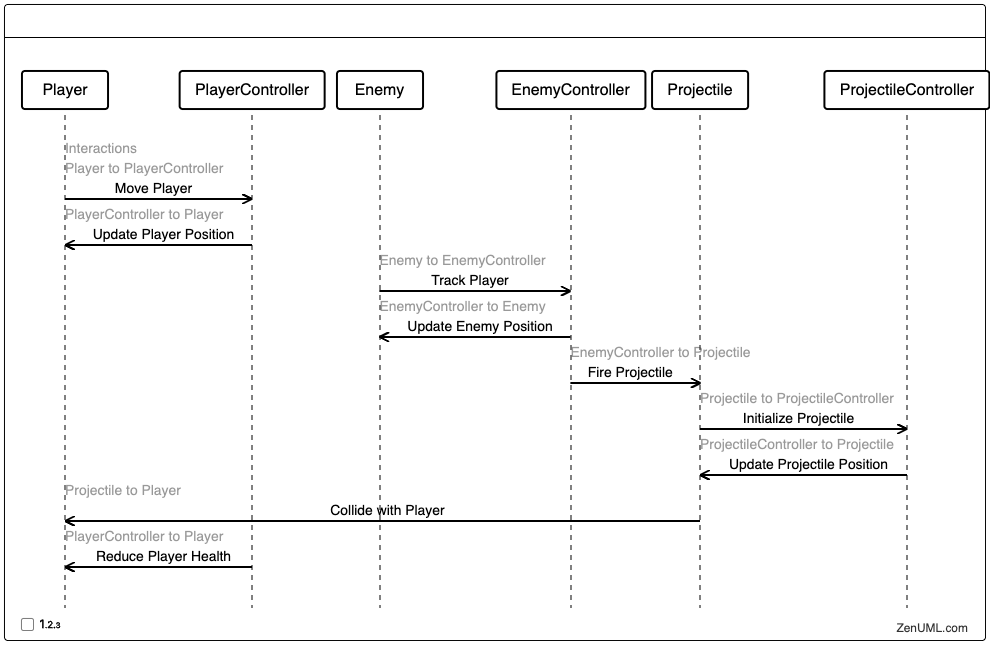
This sequence diagram depicts the interactions between the player, the enemy, and the projectile, including the movement, tracking, and collision detection processes. By visualizing these interactions, developers can better understand the game's dynamic behavior, identify potential synchronization issues, and optimize the overall entity management system.
Conclusion
Sequence diagrams are a powerful tool that can greatly enhance game development workflows. By providing a visual representation of the interactions and message exchanges between various entities, sequence diagrams facilitate improved communication, system modeling, debugging, and performance optimization.
Through the practical examples presented in this blog post, you've seen how sequence diagrams can be utilized to model player authentication and matchmaking, in-game item purchases, and complex game entity interactions. Moreover, by leveraging the ZenUML diagramming syntax, you can easily create and incorporate sequence diagrams into your game development projects.
As you continue to explore and adopt sequence diagrams in your game development process, you'll find that they can become an invaluable asset, helping you build more robust, scalable, and efficient game systems. Embrace the power of sequence diagrams, and unlock new levels of collaboration, communication, and success in your game development journey.
We invite you to share your experiences and insights in the comments below. How have you been using sequence diagrams in your game development workflows? What benefits have you observed, and what lessons have you learned? Let's continue this discussion and help each other grow as game development professionals.
Try ZenUML now!
Zenuml detailed feature roadmap available here.