Expanding the Understanding of Business Process Management
The concept of business processes is at the very heart of what makes or breaks a company's success. These processes encompass everything from the onboarding of new employees to the execution of customer orders. When processes are expertly crafted, they are the driving force behind peak operational efficiency and the delivery of exceptional customer experiences. However, as businesses expand and their operations evolve, it's common for these once streamlined processes to become overly complex or outdated, failing to meet the new demands of the company. To combat this, the practice of business process improvement is essential.
The Critical Role of Process Improvement
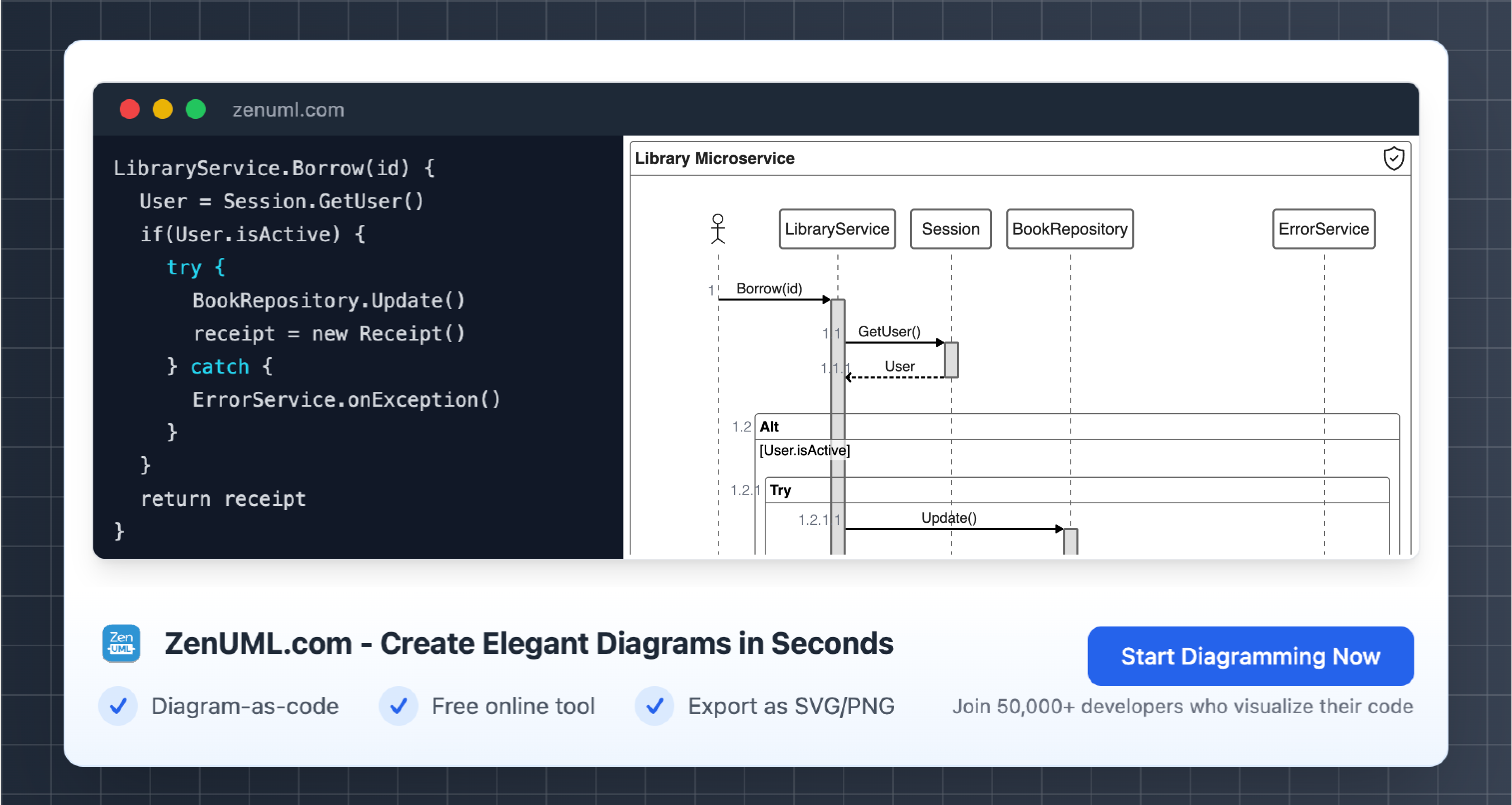
The journey of process improvement starts with a thorough analysis of the existing workflows. This is done to pinpoint bottlenecks, redundancies, or any form of inefficiencies that hinder performance. At this juncture, a sequence diagram emerges as an invaluable tool. It serves as a visual map that delineates the interaction between different parts of the organization over time. This visual aid is paramount in easily identifying areas where there are delays, redundant steps, or ambiguities in role responsibilities. Let's delve into the specifics of how sequence diagrams can significantly contribute to the process improvement initiative.
Detailed Mapping of Current Processes Utilizing Sequence Diagrams
Try ZenUML the best sequence diagram online tool now!
The initial phase in utilizing sequence diagrams is to capture the current state of affairs—or the as-is process. This requires engaging with stakeholders from across various departments to gain a comprehensive understanding of their roles and points of interaction. The resulting diagram should lay out the sequential flow of tasks and the exchange of information or data between entities, which is often denoted by arrows. These entities typically include customers, employees with particular roles, and various IT systems. This method of documentation shines a light on the intricacies of the current process.
In-Depth Analysis of the Process to Uncover Improvement Opportunities
Once the as-is sequence diagram is in hand, it's time for a critical evaluation. Key questions to ponder include: Are there repetitive tasks that add no value? Are transitions between departments causing lags? Does the process still mirror the business's strategic objectives, or has it become misaligned? Sharing the diagram with process stakeholders and seeking their input is crucial. Pairing their insights with performance metrics, such as cycle times, will spotlight the most problematic areas or steps that do not contribute value.
Ideation and Strategic Planning for Process Refinements
Moving forward, it's time to brainstorm potential modifications to simplify and enhance the process based on the identified issues. This might involve merging certain tasks, implementing automation for labor-intensive work, or altering job responsibilities. Develop a prospective sequence diagram that illustrates these enhancements and compare it with the current model. Review this proposed model collaboratively to achieve agreement on the changes. Some improvements might necessitate a complete overhaul, while others could be minor adjustments. In any case, planning and documenting the improvements in advance is crucial.
Gradual Implementation and Ongoing Evaluation of Improvements
When it's time to execute the changes, it's advisable to approach this incrementally to reduce operational disruption. Prioritize changes with the potential for the greatest impact, based on the earlier analysis. Start by testing the changes on a small scale before a widespread implementation. Vigilantly monitor key performance indicators to verify that the alterations are yielding the intended benefits. Refine the changes as necessary, drawing on insights gained from the pilot phase before proceeding with the full-scale execution.
Upholding a Culture of Persistent Process Improvement
Following the implementation, draft a new as-is sequence diagram that reflects the improved process. This serves as a means to chart progress and is a testament to the ongoing nature of process improvement. Since business needs are continually evolving, this updated diagram sets the stage for future cycles of refinement. It's beneficial to institutionalize the use of sequence diagrams and regular analysis as a standard practice within the organization to ensure that processes remain in tight alignment with business objectives.
Conclusion
In essence, sequence diagrams offer a methodical yet straightforward approach to depicting business processes from multiple angles. Their illustrative nature is adept at revealing inefficiencies that might otherwise go unnoticed. By documenting the current state and envisioned future state, sequence diagrams become vital for strategic planning, experimental testing, and ongoing monitoring of process improvements. When applied consistently, they are instrumental in keeping business workflows in sync, thereby fostering long-term business success through perpetual enhancement.
Find our more on The Ultimate Guide to Business Process Modeling
Zenuml detailed feature roadmap available here.